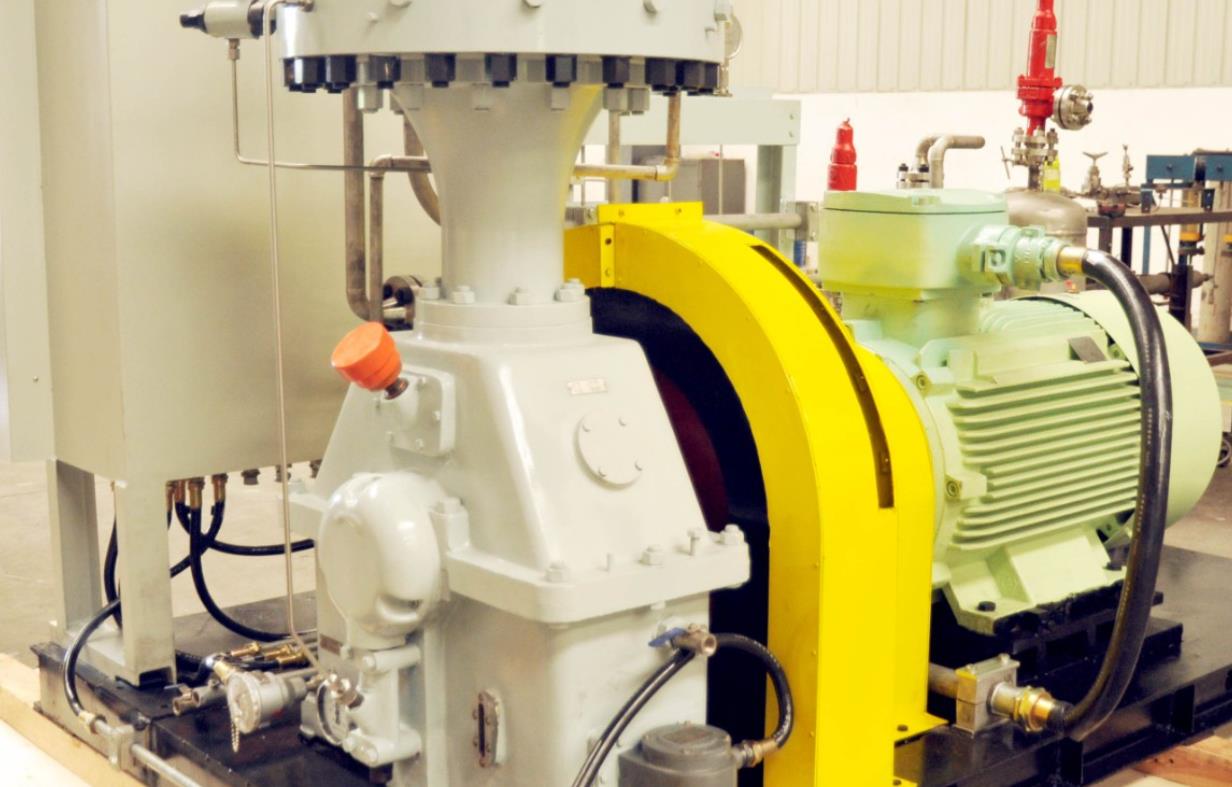
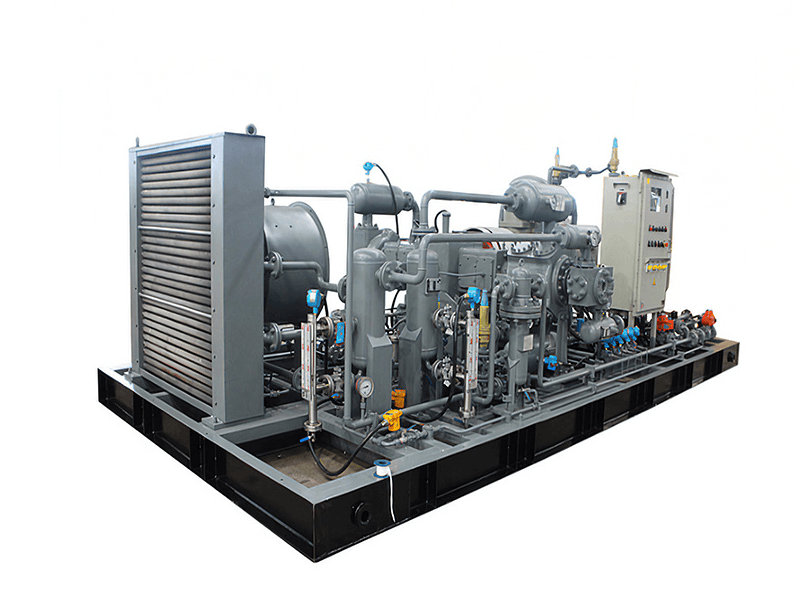
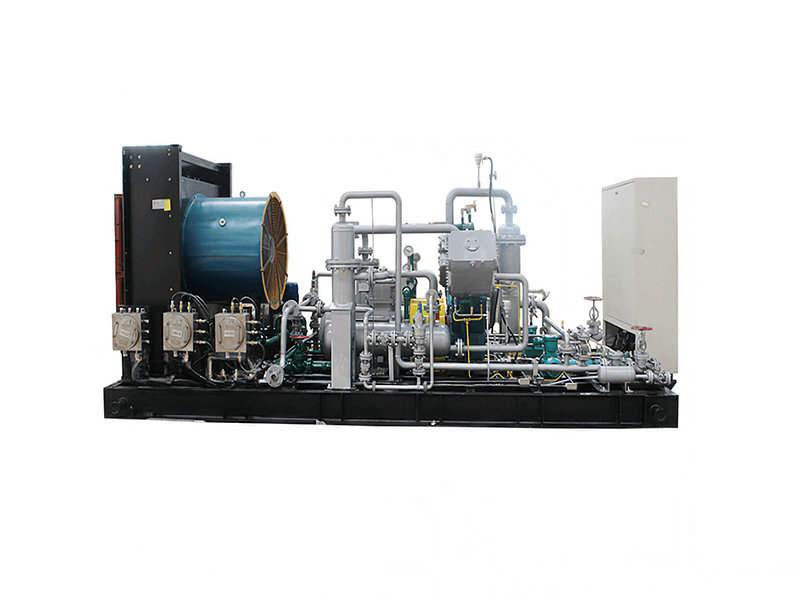
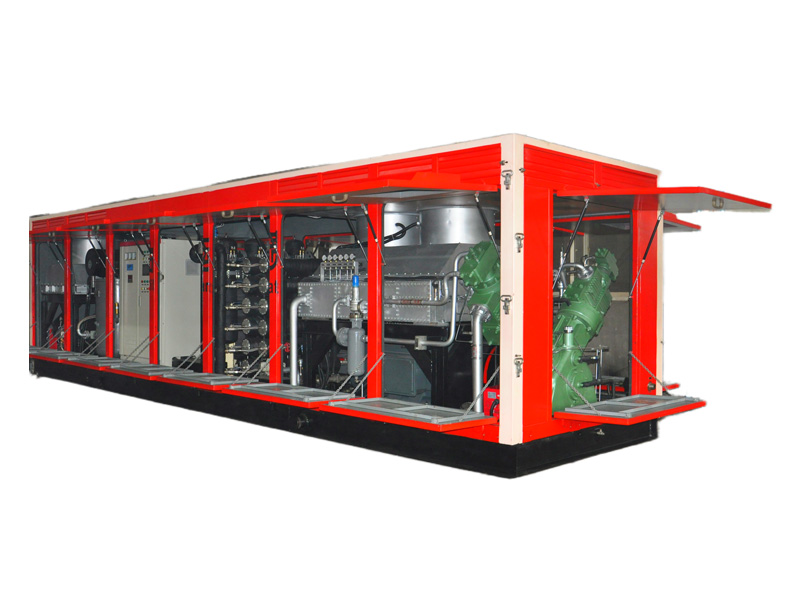
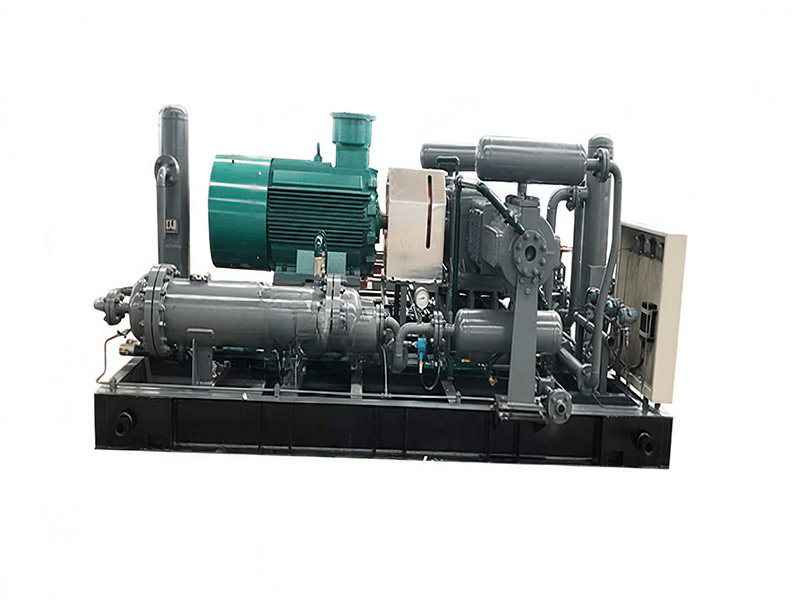
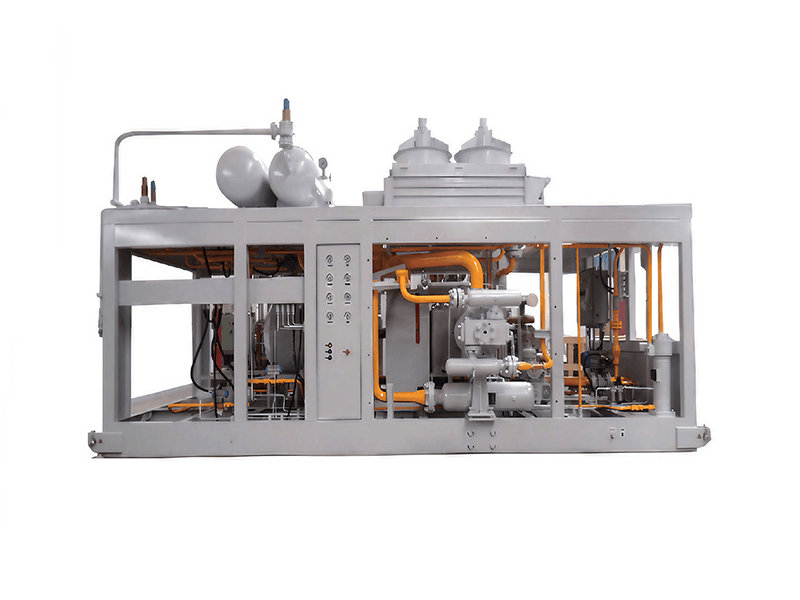
Centrifugal compressors, with their high flow capacity, energy efficiency, and operational stability, serve as core equipment in petrochemicals, LNG liquefaction, air separation units (ASU), and large-scale refrigeration. Their working principle involves high-speed impellers performing work on gases to achieve continuous pressurization, making them ideal for large-scale gas processing. This article explores key technologies, application scenarios, and case studies of centrifugal compressors. 1. Core Advantages
Dominance in large-scale industrial applications stems from:
High Flow Capacity: Single-unit flow up to tens of thousands m³/h, suitable for long-distance pipelines and integrated refineries.
Energy Efficiency: Multi-stage compression and advanced impellers (e.g., 3D blades) achieve >85% isentropic efficiency.
Low Maintenance: Non-contact dry gas seals minimize wear, enabling 24/7 operation.
High Pressure Ratio: Multi-casing or gear-driven designs achieve outlet pressures >20 MPa. 2. Key Applications & Case Studies
LNG & Pipeline Transport
Used for feed gas boosting, refrigerant cycles, and BOG (Boil-Off Gas) recovery.
Case: Gorgon LNG Project, Australia
Challenge: Offshore gas field pressure fluctuations (4–8 MPa).
Solution: Multi-stage centrifugal compressors with VFD and anti-surge control.
Result: 16 MTPA capacity, 88% efficiency, 12% energy reduction. 2.2 Petrochemicals & Hydroprocessing
Critical for hydrogen recycling and rich gas compression in FCC/hydrocracking.
Case: Zhejiang Petrochemical Refinery (40 MMTPA), China
Requirement: Hydrogen compression from 2.5→18 MPa (50,000 Nm³/h).
Technology: Barrel-type compressor (BB) with dry gas seals and real-time monitoring.
Outcome: >8,000 hours uninterrupted operation, 99.5% H₂ recovery. 2.3 ASU & Industrial Refrigeration
Provides compressed air for ASUs or drives ammonia cycles in steel/electronics.

Case: Middle East Steel Plant ASU
Requirement: 120,000 Nm³/h air at 0.6 MPa (99.6% O₂ purity).
Innovation: Axial inlet + 3D impeller reduced energy consumption by 8%. 3. Technical Challenges & Innovations
Surge Control & AI Integration
Issue: Surge risk under high pressure ratios.
Solutions: Active anti-surge valves (e.g., Honeywell CCC), AI predictive maintenance (e.g., Siemens MindSphere). 3.2 Materials & Coatings
High-Temp: Nickel-alloy impellers (Inconel 718) withstand 700°C (ethylene cracker gas).
Corrosion Resistance: Ceramic coatings for sour gas (Middle East fields). 3.3 Decarbonization & Efficiency
CCUS: Supercritical CO₂ compression (e.g., Sleipner Field, 1 Mt/year).
Waste Heat Recovery: ORC systems for power generation. 4. Future Outlook
Hydrogen Economy: 30 MPa hydrogen transport (e.g., HyDeal Europe).
Modularization: Skid-mounted units for floating LNG/distributed energy. Centrifugal compressors drive industrial efficiency through unmatched large-scale gas handling. Integration with digitalization and low-carbon technologies will further expand their frontiers.