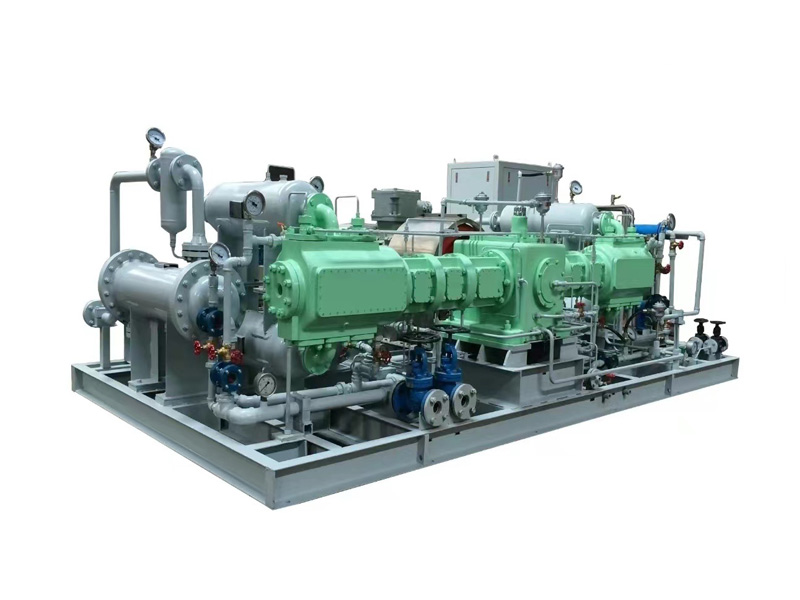
Piston compressors represent one of the oldest technological forms in the field of industrial compression. Since their inception during the mid-19th century Industrial Revolution, they have undergone numerous technological innovations and continue to maintain important positions in various industrial scenarios. According to the international standard ISO 13684, piston compressors are defined as "positive displacement compressors that achieve gas compression through the reciprocating motion of pistons within cylinders." Their reliable working principles and exceptional high-pressure performance make them irreplaceable key equipment in specific industrial applications.
Working Principle and Technical Characteristics
The working principle of piston compressors is based on positive displacement. A crank-connecting rod mechanism converts the rotational motion of the motor into the reciprocating motion of the piston. When the piston moves toward the crankcase, the volume inside the cylinder increases, creating a negative pressure that opens the intake valve, allowing gas to be sucked into the cylinder. When the piston moves toward the cylinder head, the volume decreases, compressing the gas. When the pressure reaches the discharge pressure, the exhaust valve opens, releasing the compressed gas. This operational method gives piston compressors two distinctive characteristics: first, the ability to generate extremely high outlet pressures, up to 100 MPa; second, maintaining high efficiency even under low-flow conditions, with volumetric efficiency reaching 85%–95%.
Modern piston compressors incorporate multiple technological innovations: labyrinth seal technology for oil-free compression; hydraulic drive systems for smooth power transmission; double-acting cylinder designs to improve工作效率; and multi-stage compression with intercooling systems to control discharge temperatures within safe ranges. These innovations significantly enhance the performance of piston compressors while preserving their traditional advantages.
Gas Adaptability and Application Fields
Piston compressors demonstrate excellent performance in terms of gas adaptability. They are not only suitable for conventional air compression but can also efficiently handle inert and special gases such as nitrogen, hydrogen, and argon. Depending on the gas properties, appropriate materials and technical solutions must be adopted: oil-free designs and oxidation-resistant materials for oxygen compression; special sealing structures and leak prevention measures for hydrogen compression; and stainless steel or special alloy materials for corrosive gases.
In ultra-high-pressure applications, piston compressors offer significant advantages. For example, in breathing air cylinder filling, gases need to be compressed to over 30 MPa using three or four-stage compression designs; in industrial gas liquefaction processes, pressures of 20–50 MPa require special valves and enhanced cooling systems; in the petrochemical industry, some processes even require working pressures exceeding 70 MPa, utilizing ultra-high-pressure cylinders and special sealing technologies. In these application scenarios, piston compressors are currently the most reliable choice.

Technical Advantages and Limitations
The main advantages of piston compressors include: a wide pressure range, from vacuum to ultra-high pressure (over 100 MPa); high efficiency, particularly under partial load conditions; strong adaptability to various special gases; and relatively simple structure with convenient maintenance. However, this type of compressor also has certain limitations: due to their reciprocating working principle, equipment operation generates significant vibration and noise, usually requiring foundation reinforcement and sound insulation measures. Vibration velocity must be controlled below 4.5 mm/s, and noise levels need to be controlled within 85 dB(A) using acoustic enclosures.
Additionally, piston compressors have many moving parts and require regular maintenance, including piston ring replacement, valve inspection, and connecting rod bearing checks. The maintenance cycle is typically 4,000–8,000 operating hours, depending on working pressure and gas properties. For high-pressure applications, non-destructive testing is also required periodically, including magnetic particle inspection of cylinder inner walls and ultrasonic testing of crankshafts.
Selection Guide and Technical Specifications
When selecting a piston compressor, several key technical parameters need to be considered: working pressure range, displacement requirements, gas properties, and environmental conditions. For high-pressure applications, a multi-stage compression design is recommended, with a compression ratio generally controlled between 3:1 and 4:1 per stage. The cooling system needs to be designed according to discharge temperature requirements, usually employing water cooling or forced air cooling.
Equipment manufacturing must comply with relevant technical standards: pressure vessels according to ASME BPVC Section VIII; safety valve settings following API 526; vibration control per ISO 10816-3; and noise control meeting OSHA 29 CFR 1910.95. For special gas compression, corresponding industry specifications must also be followed, such as EIGA IGC 33/18 for oxygen compression.
Innovation Development Trends
Modern piston compressor technology is advancing toward greater efficiency and intelligence. Composite material pistons reduce moving mass and increase operating speeds; intelligent control systems enable predictive maintenance; laser surface treatment technology improves cylinder wear resistance; and new sealing materials extend maintenance cycles. These innovative technologies allow piston compressors to better adapt to modern industrial needs while maintaining their traditional advantages.
In summary, piston compressors are particularly suitable for the following conditions: applications requiring outlet pressures above 15 MPa; processes with small gas handling capacities (typically less than 20 m³/min); industrial scenarios requiring the handling of special gases; and applications demanding high efficiency and good partial load performance.
If you need further information about the technical characteristics of piston compressors or require equipment selection for specific working conditions, our engineering technical team can provide professional consultation. We offer complete solutions, including process calculations, equipment selection, installation guidance, and maintenance services. Please contact us through the official website to obtain detailed technical solutions and schedule on-site inspections and technical exchanges.
Note: The technical parameters described in this article are based on industry general standards. Specific equipment performance is subject to the technical data provided by the manufacturer. Equipment selection recommendations should be made after detailed calculations and evaluations by professional technical personnel, considering local environmental conditions and safety regulations. Operation and maintenance of ultra-high-pressure equipment must be performed by specially trained personnel.